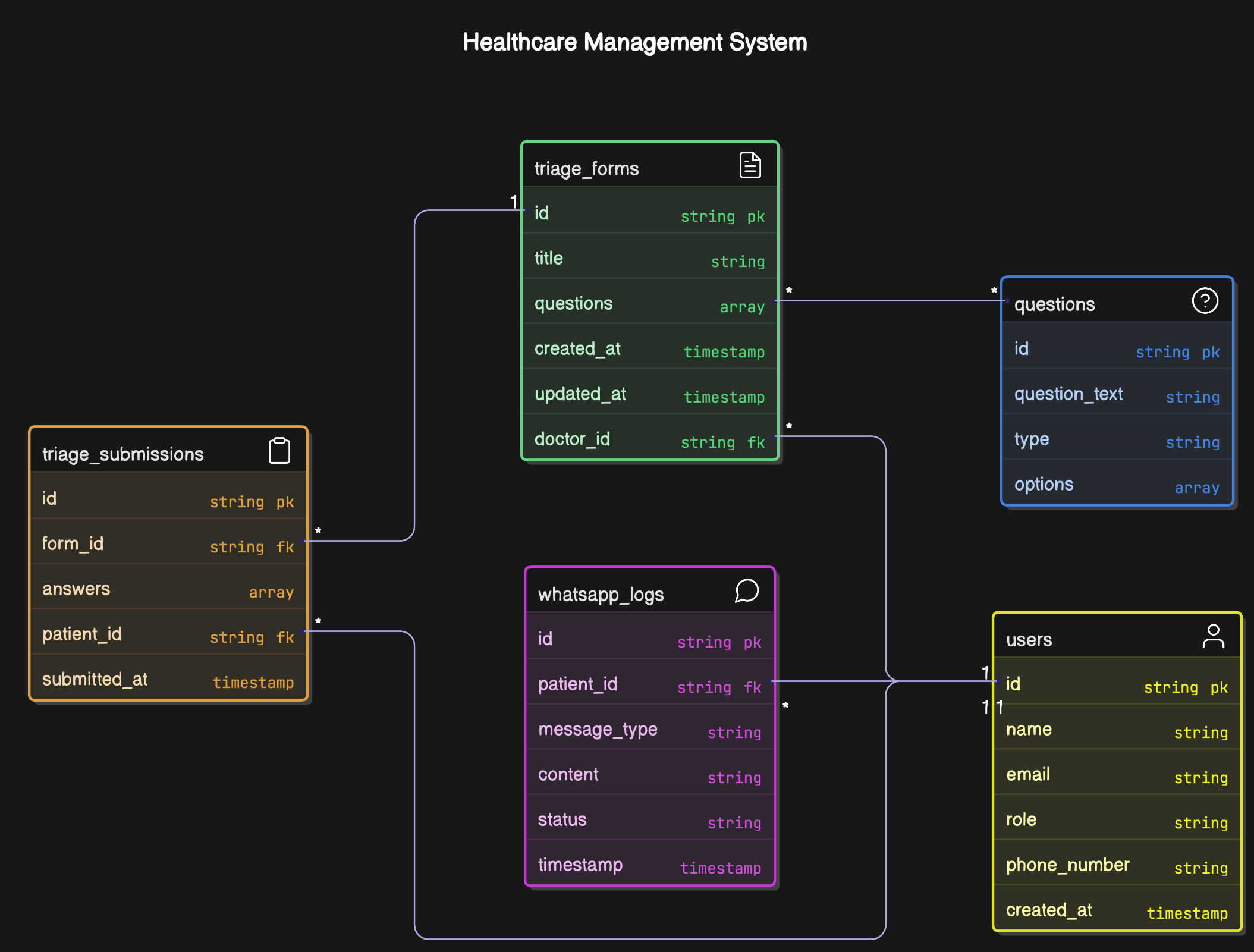
🧠 Database Schema Design Justification (MongoDB)
This document outlines the rationale behind the MongoDB schema design for the triage backend system. The database structure balances flexibility, performance, and scalability, while supporting the current and future needs of doctors and patients.
📦 NoSQL Approach with MongoDB
MongoDB is a document-based NoSQL database. It is chosen for this system because:
- Triage forms and their questions may evolve over time and vary per doctor.
- Patients' answers can be stored as nested data without requiring rigid relational modeling.
- High flexibility in how we store and query semi-structured health data.
- Excellent support in both IBM Cloud and AWS, aiding cloud portability.
Collections
{
_id: ObjectId,
name: String,
email: String,
role: "doctor" | "patient",
phone_number: String,
created_at: Date
},
{
_id: ObjectId,
doctor_id: ObjectId (ref to users),
title: String,
questions: [Embedded Array or Question References],
created_at: Date,
updated_at: Date
},
{
_id: ObjectId,
question_text: String,
type: "text" | "radio" | "checkbox",
options: [String]
},
{
_id: ObjectId,
form_id: ObjectId (ref to triage_forms),
patient_id: ObjectId (ref to users),
answers: [Array of Answers],
submitted_at: Date
},
{
_id: ObjectId,
patient_id: ObjectId (ref to users),
message_type: "sent" | "received",
content: String,
status: "pending" | "delivered" | "read",
timestamp: Date
}