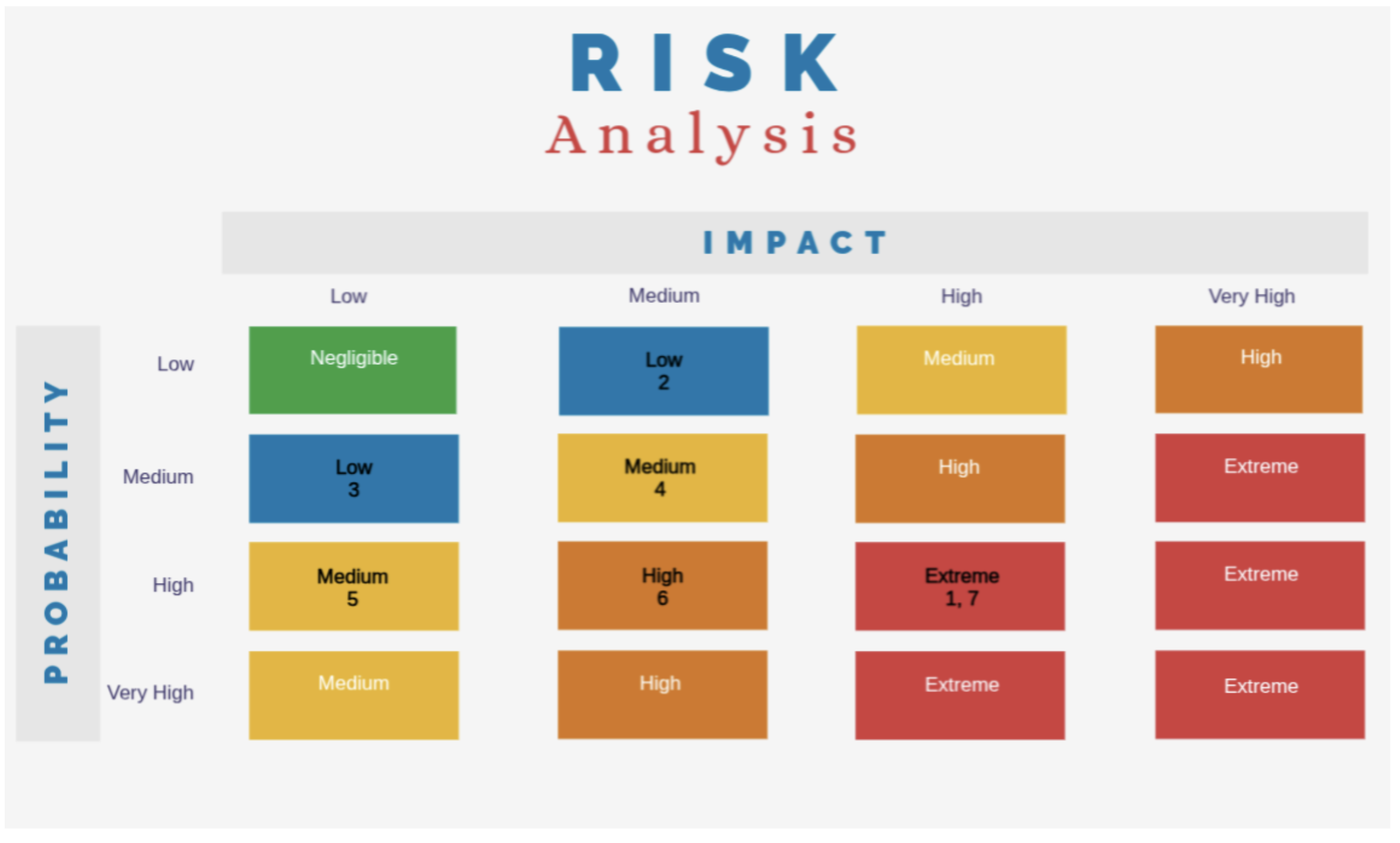
risk_matrix
Risk Matrix
-
Initial resistance from patients to using the chatbot: Some patients, especially older ones, may prefer human interaction. A user-friendly interface and clear guidance can help ease adoption.
-
Need for minor interface adjustments to improve usability: Usability issues, such as navigation difficulties or accessibility concerns, may require continuous improvements based on user feedback.
-
Difficulty integrating with legacy hospital systems: Many hospitals use outdated EMR systems that may not support easy integration, requiring custom solutions for interoperability.
-
Difficulty in hospital adoption of the solution: Hospitals may resist change due to workflow disruptions or compliance concerns. Demonstrating efficiency and regulatory compliance will be key.
-
IBM Watson training may require continuous adjustments: AI performance depends on high-quality training data, requiring ongoing refinement to ensure accurate and relevant responses.
-
Challenges in collecting and validating clinical data for model training: Medical data is often restricted due to privacy regulations, making data collection and validation a challenge for model accuracy.
-
Strong resistance from hospitals in adopting the solution: Hospitals may be skeptical about AI-driven triage due to liability concerns. Trust can be built through pilot programs and real-world case studies.
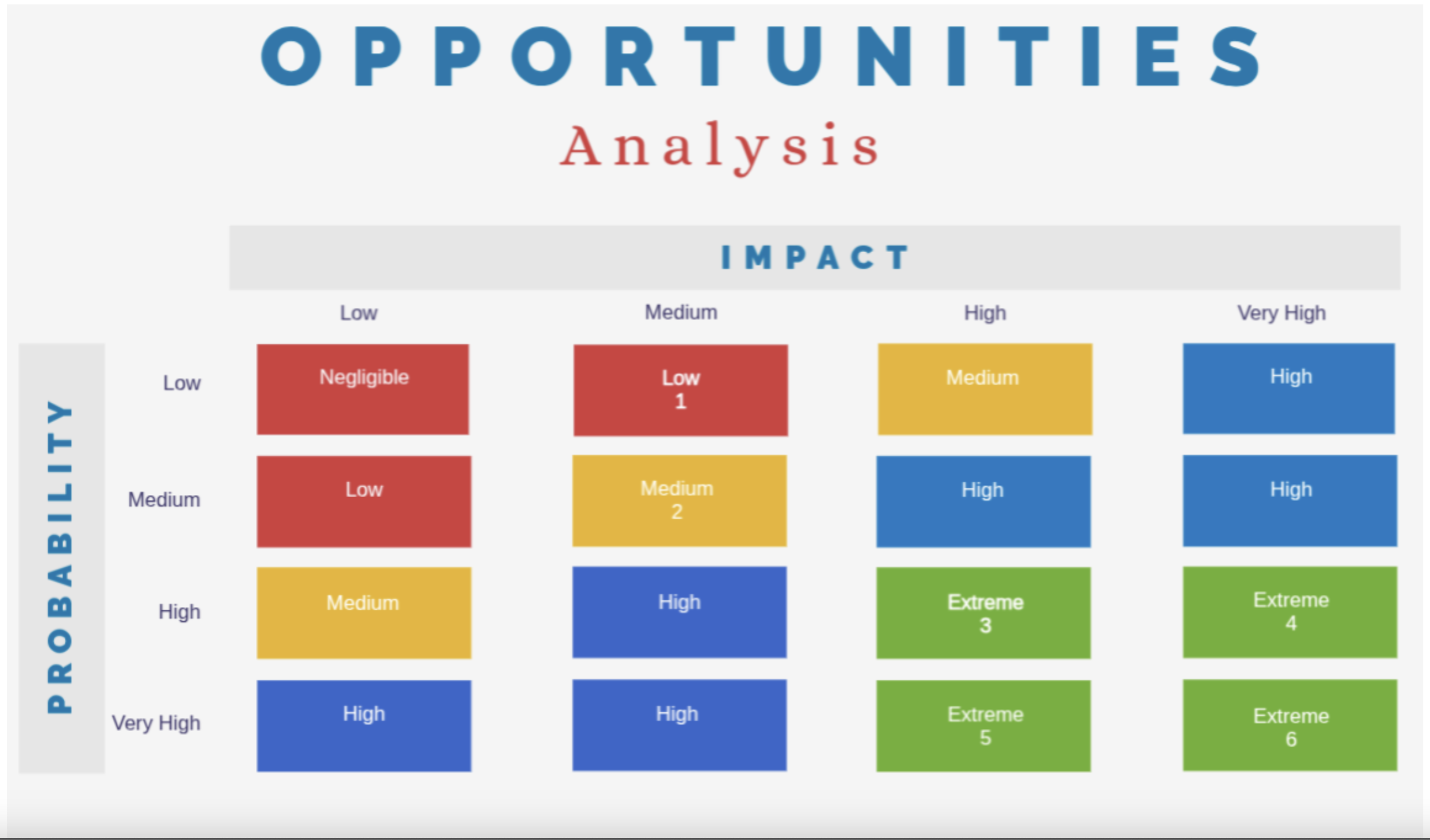
Opportunity Matrix
-
Gradual acceptance of the technology by healthcare professionals: As AI solutions become more common in healthcare, professionals may increasingly trust and adopt AI-driven triage systems.
-
Potential expansion to private hospital networks: Private hospitals, looking to optimize efficiency and reduce costs, may be more open to adopting AI-driven triage solutions.
-
Significant optimization of triage flow in medium-sized hospitals: Automating triage can streamline hospital workflows, reducing bottlenecks and improving patient flow in mid-sized facilities.
-
Large-scale reduction in healthcare professionals' workload: By handling initial patient assessments, the system allows nurses and doctors to focus on critical cases, improving overall efficiency.
-
Large-scale hospital triage automation: The solution can be expanded to multiple hospitals, standardizing and accelerating triage processes across different institutions.
-
Transformation of the triage model in São Paulo with potential national adoption: If successful in São Paulo, the model could serve as a blueprint for implementation in other cities, potentially revolutionizing triage nationwide.